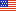
Catalyzing Commercialization: Two-Dimensional Materials for Versatile Biosensing
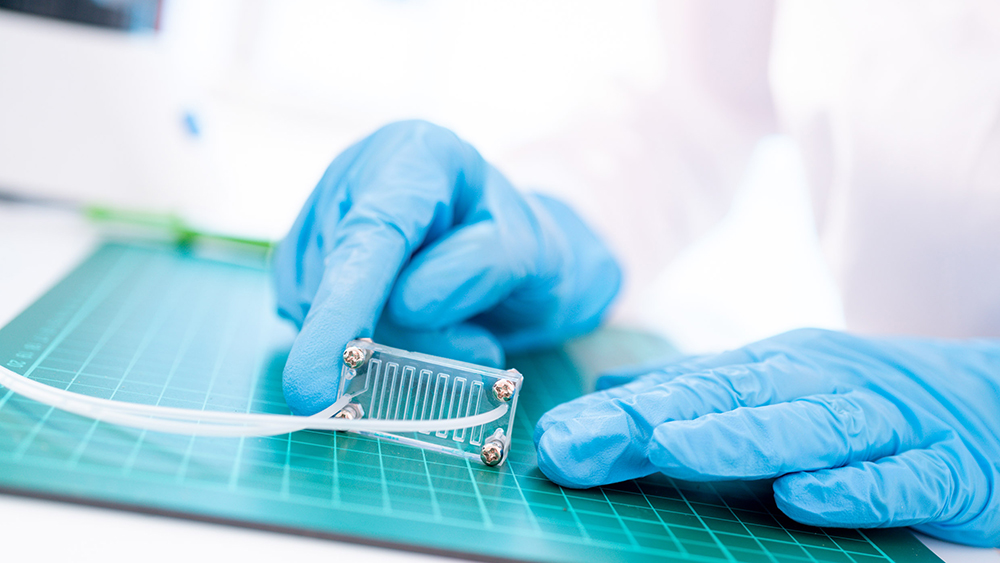
As modern medicine becomes more personalized and less centralized, the need for scalable and tunable platforms for next-generation point-of-care biosensors remains an ongoing research objective. One promising technology for point-of-care analysis is electrochemical sensors, which are portable, ultrasensitive, and inexpensive. Electrochemical sensors are compatible with integrated circuit technology, enabling integration of sensors with the necessary electronic circuitry for data acquisition, processing, and transfer.
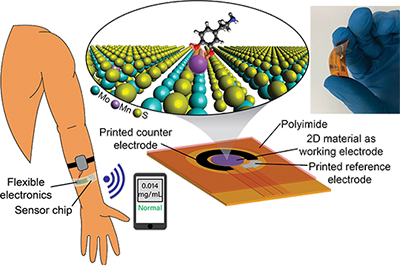
Learn MoreCatalyzing Commercialization: Novel Concrete Wall Panels Lower a Building’s Energy Footprint
About 20% of total energy consumption in the U.S. is used for the heating and cooling of buildings using conventional sources like fossil fuels. While standard thermal insulation, with its low thermal conductivity, can help mitigate heating/cooling loss, researchers have sought to incorporate thermal storage capacity within the building envelope to better control the temperature variations across building walls.
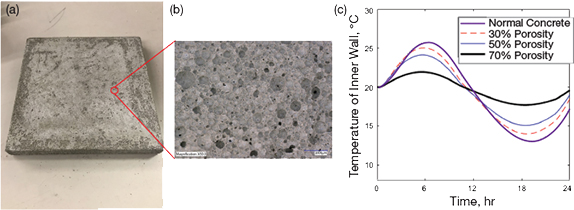
Learn MoreNew Insights May Improve Performance of Medicine-Producing Cells
Samples waiting to be analyzed on the mass spectrometer to quantify the incorporation of stable isotopes of carbon, which provides new insights into how nutrients are metabolized by CHO cells. Credit: Maciek Antoniewicz, University of MichiganJust like us, cells need to watch what they eat.
Learn MoreNew Technology for Isolating Single Cells Opens the Door for Fast and Precise Experiments and Treatments
Credit: luchschenF/Shutterstock. Singling out a diseased or mutated cell and identifying which treatment option is most effective can be cumbersome, expensive, and time-consuming.
Learn MoreTest Helps ‘Rubber Meet the Road’ in Wet Driving Conditions
Credit: Siamak Farhad, Mechanical Engnieering Department, University of AkronMore than 300,000 people are injured and about 4,000 die each year in car crashes that occur on roads with wet pavement, according to the U.S. Department of Transportation.
Learn More