Center
Focus Area
Universities
Year Est.
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2015
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
- Advanced Materials
2011
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2014
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
- Advanced Electronics
2013
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2010
2022
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2015
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2011
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2009
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2014
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2018
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
- Energy and Environment
2021
-
Advanced Materials
- Advanced Materials (Primary Area)
2010
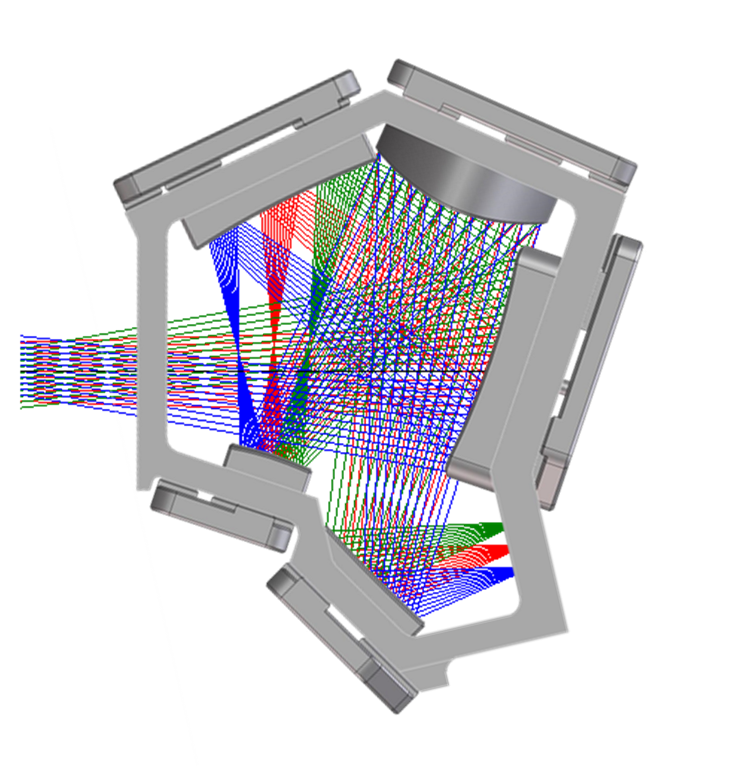
Freeform Enables Compact Spectrometer Designs
2D raytrace of the five-mirror freeform viewfinder design superimposed on a 3D model of the system housing.
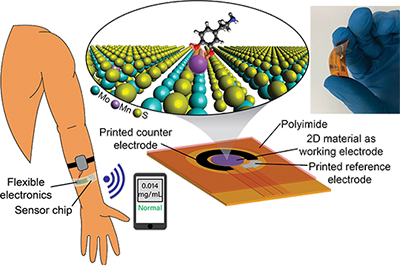
Learn MoreCatalyzing Commercialization: Two-Dimensional Materials for Versatile Biosensing
As modern medicine becomes more personalized and less centralized, the need for scalable and tunable platforms for next-generation point-of-care biosensors remains an ongoing research objective. One promising technology for point-of-care analysis is electrochemical sensors, which are portable, ultrasensitive, and inexpensive. Electrochemical sensors are compatible with integrated circuit technology, enabling integration of sensors with the necessary electronic circuitry for data acquisition, processing, and transfer.
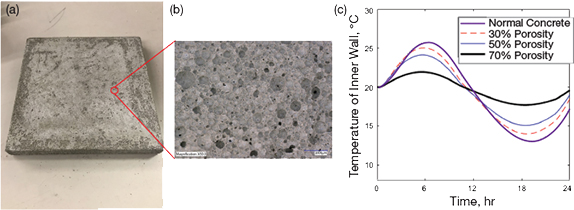
Learn MoreCatalyzing Commercialization: Novel Concrete Wall Panels Lower a Building’s Energy Footprint
About 20% of total energy consumption in the U.S. is used for the heating and cooling of buildings using conventional sources like fossil fuels. While standard thermal insulation, with its low thermal conductivity, can help mitigate heating/cooling loss, researchers have sought to incorporate thermal storage capacity within the building envelope to better control the temperature variations across building walls.
Learn More